Investigating the effect of modeling exchange rate fluctuations in creating the advantage of foreign trade in the framework of the resistance economy system
Keywords:
modeling, fluctuations, exchange rate, creation, advantage, foreign trade, resistance economy systemAbstract
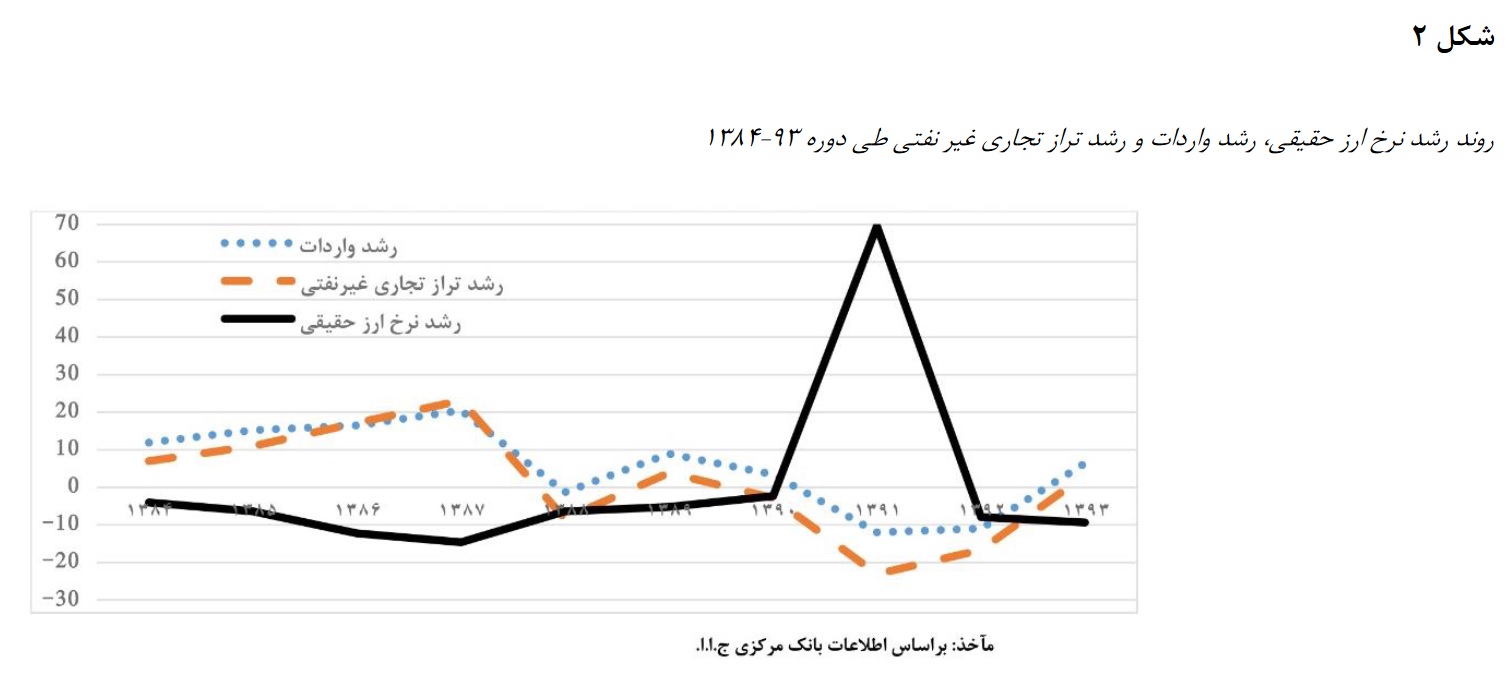
The purpose of this research is to model exchange rate fluctuations in creating the advantage of foreign trade in the framework of a resistance economy system, and we are looking for an answer to the question of whether changes in exchange rates affect the return on assets in the framework of an asset pricing model based on foreign trade in the economic system. Is resistance effective? And if it is effective, is this effect positive or negative? Resistance economics is a literature that has been proposed to deal with international sanctions. Iran's economy must now take steps based on the right principles so that it can overcome international sanctions and turn the threat of sanctions into an opportunity. Those principles and foundations that Iran's economy should have have created a literature called resistance economy. Monetary and financial policies should be specified in this economic literature and we should always answer the question of what we are looking for in the policies we do. In order to understand how monetary and financial policies, etc. should be and what direction they should follow, we must first have a correct understanding of Iran's economy and the main problem of Iran's economy. For example, a policy is implemented with a goal, but then it becomes clear that not only have we not reached the goal, but we have moved away from it. Based on this, in the literature of resistance economy, first of all, we should know what is the main problem of Iran's economy? After that, we have to identify the right way to deal with the problem, and that is where we can talk about monetary and financial policies and all kinds of other policies. Exchange rate regimes and its fluctuations can have serious consequences for countries' economies. Theoretically, the exchange rate affects inflation, foreign trade, capital account and other key macroeconomic variables. The results of the trade balance model show that the nominal exchange rate has a negative effect on the trade balance. While the real exchange rate has a positive relationship with the trade balance. For example, we can refer to Iran between 1959 and 2003, where the devaluation of the national currency has increased the motivation to strengthen and produce non-oil exports. thousand million dollars compared to 1400. In this research, we are looking for an answer to the question: modeling exchange rate fluctuations on creating an advantage. What are the effects of foreign trade in the framework of the resistance economy system?
Downloads