اثر ساختاربندی فرهنگی (اسلامی، غربی، ایرانی و محلی) بر کنش فرهنگی (قانونپذیری، مسئولیتپذیری، رعایت فرهنگ شهرنشینی و سرمایه اجتماعی) در بین اعضای هیئت علمی دانشگاه پیام نور کشور
کلمات کلیدی:
ساختاربندی فرهنگی, کنش فرهنگی, قانونپذیری, مسئولیتپذیری, فرهنگ شهرنشینی, سرمایه اجتماعی, دانشگاه پیام نورچکیده
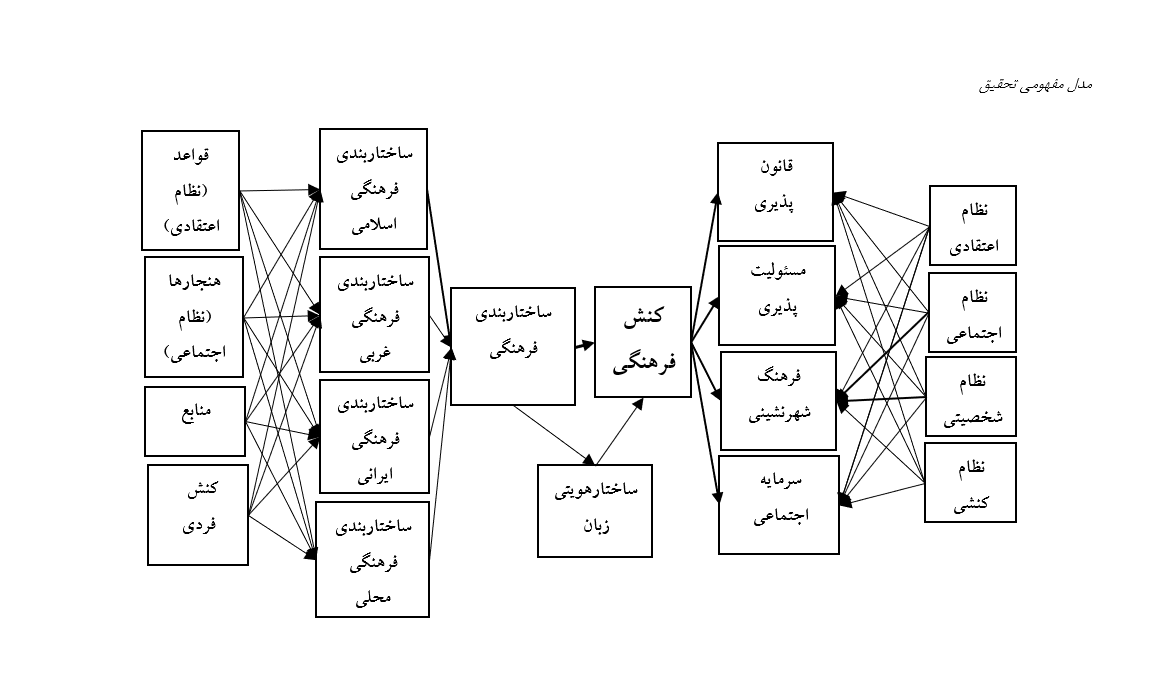
هدف این پژوهش بررسی تأثیر ساختاربندیهای فرهنگی (اسلامی، غربی، ایرانی و محلی) بر ابعاد کنش فرهنگی شامل قانونپذیری، مسئولیتپذیری، رعایت فرهنگ شهرنشینی و سرمایه اجتماعی در بین اعضای هیئت علمی دانشگاه پیام نور کشور است. این پژوهش با رویکرد ترکیبی (کیفی و کمی) انجام شده است. در بخش کیفی از روش دلفی با مشارکت 17 نفر از خبرگان استفاده شد تا شاخصهای مرتبط با متغیرها استخراج و اعتبارسنجی شوند. در بخش کمی، پرسشنامهای بر اساس شاخصهای تأییدشده طراحی شد و دادهها از نمونهای متشکل از 351 نفر از اعضای هیئت علمی دانشگاه پیام نور سراسر کشور گردآوری شد. تحلیل دادهها با استفاده از نرمافزارهای SPSS و AMOS و روش معادلات ساختاری صورت گرفت. نتایج نشان داد ساختاربندی فرهنگی ایرانی بیشترین تأثیر را بر کنشهای فرهنگی دارد. ساختاربندی فرهنگی اسلامی در ایجاد مسئولیتپذیری و سرمایه اجتماعی نقش تعیینکنندهای دارد. ساختاربندی محلی تأثیر قابلتوجهی بر فرهنگ شهرنشینی و قانونپذیری دارد. ساختاربندی غربی بیشتر بهصورت غیرمستقیم و از طریق تعامل با سایر ساختارها بر متغیرهای فرهنگی تأثیر میگذارد. ضرایب مسیرها معنادار بوده و مدل نهایی دارای برازش مناسب است. یافتهها بر اهمیت شناخت تفاوتهای فرهنگی در شکلگیری کنشهای اجتماعی تأکید دارد. تقویت ساختارهای فرهنگی بومی و دینی و بهویژه ایرانی میتواند زمینهساز توسعه رفتارهای اجتماعی مطلوب در نظام آموزش عالی باشد.
دانلودها
مراجع
Azkia, M., & Ghaffari, G. (1999). Sociology of Development. Kalmeh Publishing.
Bahripour, A. (2013). Bias in the social responsibility of citizens and its effective factors: A case study of citizens of Kashan Allameh Tabataba'i University, Faculty of Social Sciences]. Tehran.
Barzegari, F., & Chaharganbadi, H. (2013). Investigating the rate of law-breaking and its effective factors in Kerman city. Law Enforcement Knowledge Quarterly, 4(5), 63-77.
Behravan, H., & Behravan, N. (2011). Sociological causes of high-risk driving in Mashhad. Journal of Social Security Studies(28), 109-142.
Bourdieu, P. (1979). The Inheritors: French Students and their Relations to Culture. University of Chicago Press.
Fakoohi, N. (2009). Strengthening citizen ethics as a way to transition to participatory democracy. Iranian Journal of Social Studies, 2(2).
Falks, C. (2003). Citizenship. Kimia.
Gottfredson, M., & Hirschi, T. (1990). A general theory of crime. Standford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1515/9781503621794
Hashemianfar, S., & Ganji, M. (2009). An analysis of citizenship culture in Isfahan city. Quarterly Journal of Applied Sociology, 20(33).
Heidari, A., Rezadoust, K., & Foroutan Kia, S. (2012). Institutional anomie theory and law-breaking: A case study of students at Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. Iranian Journal of Social Issues, 3(2), 3-59.
Hemmati, R., & Ahmadi, V. (2012). A sociological analysis of the status of citizenship culture and its explanatory factors in Ilam city. Quarterly Journal of Social Welfare and Development Planning(18).
Hosseini Mehrabadi, H. S., & Asghari, M. (2021). Investigating the relationship between family performance and responsibility in female students of Qom University. Pooyesh in Educational Sciences and Counseling, 7(15), 168-186.
Junger, M., & Haen Marshall, I. (1997). The inter-ethnic generalizability of social control theory: An empirical test. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 34, 79-112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022427897034001005
Karami, M. (2017). Investigating the causal relationship between professional ethics, organizational ethics, ethical leadership, and social responsibility with the mediation of social health among second-grade high school teachers in Kurdistan province Faculty of Literature and Humanities]. Urmia.
Karimian, M., & Zare'i, G. (2017). Factors effective on youth modernism in urban culture. Urban Management Journal, 16(46).
Khosravi, S., Mohseni Tabrizi, A., & Aghajani Marsa, H. (2021). A sociological explanation of the share of social capital in social mobility. Iranian Journal of Social Development Studies, 13(2), 99-113.
Longshore, D., Chang, E., Hsieh, S., Hsieh, S., & Messina, N. (2004). Self-control and social bonds: A combined control perspective on deviance. 542-564. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011128703260684
Mirzaei, A., Ahmadi, Y., Bokharaei, A., & Naebi, H. (2017). Law-breaking and social bonds: A case study: Ahvaz city. Journal of Cultural Sociology Research, 8(3), 6-31.
Moradi, M. (2018). A sociological study of the effect of quality of life on the social responsibility of youth: A case study of Kermanshah city Kharazmi University, Faculty of Literature and Humanities].
Mousavi, M. T. (2007). Measuring the social capital of youth in Iran.
Movahed, M., Salehi, R., & Hosseini, M. (2013). Comparing the relationship between cultural factors and the level of responsibility among adolescents in Baneh and Qorveh cities. Journal of Applied Sociology(38), 79-98.
Najafzadeh Oujqaz, Z., Karimzadeh, S., & Nazem, F. (2021). Presenting a model for improving the level of social responsibility of faculty members of Islamic Azad University (Tehran province) based on professional ethics and job performance. Productivity Management (Beyond Management), 15(2, Consecutive No. 57), 259-279.
Nikzad, A. (2019). Investigating the relationship between urban culture and interactions in urban spaces in Malayer city Payam Noor University of Hamadan province, Hamadan Payam Noor Center].
Nouri, J., Bokharaei, A., & Sinaei, S. A. (2020). A sociological study of the relationship between social capital and the sense of social security. Law Enforcement Order and Security Research Journal, 13(3, Consecutive No. 51), 203-228.
Pirahari Nir, A. (2020). Investigating the relationship between cultural and social factors and law-breaking in Semnan city. Social Order Journal, 12(1), 141-162.
Sharbatiyan, M., Jahanshiri, J., & Omrani, M. (2021). Sociological analysis of the relationship between effective factors on law-breaking (Case study: 20-34 year-old youths in Mashhad). Social Order Journal, 13(2), 81-114.
Shirdel, E., Hami Kargar, F., & Anjum Shoa, F. (2021). The relationship between social capital and lifestyle with national identity of adolescent girls in Kerman city. Journal of National Studies, 22(2), 69-87.
Shojaei Zand, A. (2000). Anti-order and law-breaking. (14), 32-34.
Sobhannejad, M. (2000). Social responsibility in the current curriculum of Iranian elementary schools and designing for the future Tarbiat Modares University].
Sohanian Haghighi, M., Fouladian, M., & Akbari, H. (2019). Comparative analysis of factors effective on law-breaking and law-violation in Iranian provinces based on fuzzy logic. Journal of Iranian Sociology, 20(4), 3-32.
Taghizadeh, S. (2015). A comparative study of urban culture among affluent and non-affluent families in District 2 of Tehran city based on Norbert Elias's theory
Talebi Panbeh Choleh, G. A., Zolfaghari, R., & Parsa Moein, K. (2021). Evaluation of social responsibility components of Islamic Azad University of Mazandaran. Journal of Jundishapur Education Development, 12(2), 521-531.
Tizroo Tooli, F. (2017). Comparing the effect of spiritual and personal intelligence training on the adjustment, responsibility, and lawfulness of 14-16 year-old students Islamic Azad University, Faculty of Humanities]. Ardabil.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Ali Reza Mokhtari (Corresponding Author)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.







