Analysis of the effects of globalization on citizenship rights in Tehran
Keywords:
حقوق شهروندی، جهانی شدن، حقوق مدنی، حقوق اجتماعی، تهران.Abstract
The purpose of this article is to investigate the effects of globalization on citizenship rights in Tehran. Citizenship rights are one of the main indicators of civil society, which is affected by various factors, including globalization. For this purpose, the theory of Marshall and Anthony Giddens was used as a theoretical framework. The research method is a survey, and the statistical population is people aged 20 and older in Tehran. The sampling method is a multi-stage cluster proportional to the size of the population of each of the 22 districts of Tehran, and the sample size is 384 people according to Morgan's table. The tool for data collection is a researcher-made questionnaire. The method of data analysis is Pearson's correlation coefficient and regression analysis using SPSS software. Face validity was used to measure validity and the measurement tool has the required reliability and the variable reliability of citizenship rights is 0.876 and globalization is 0.823.
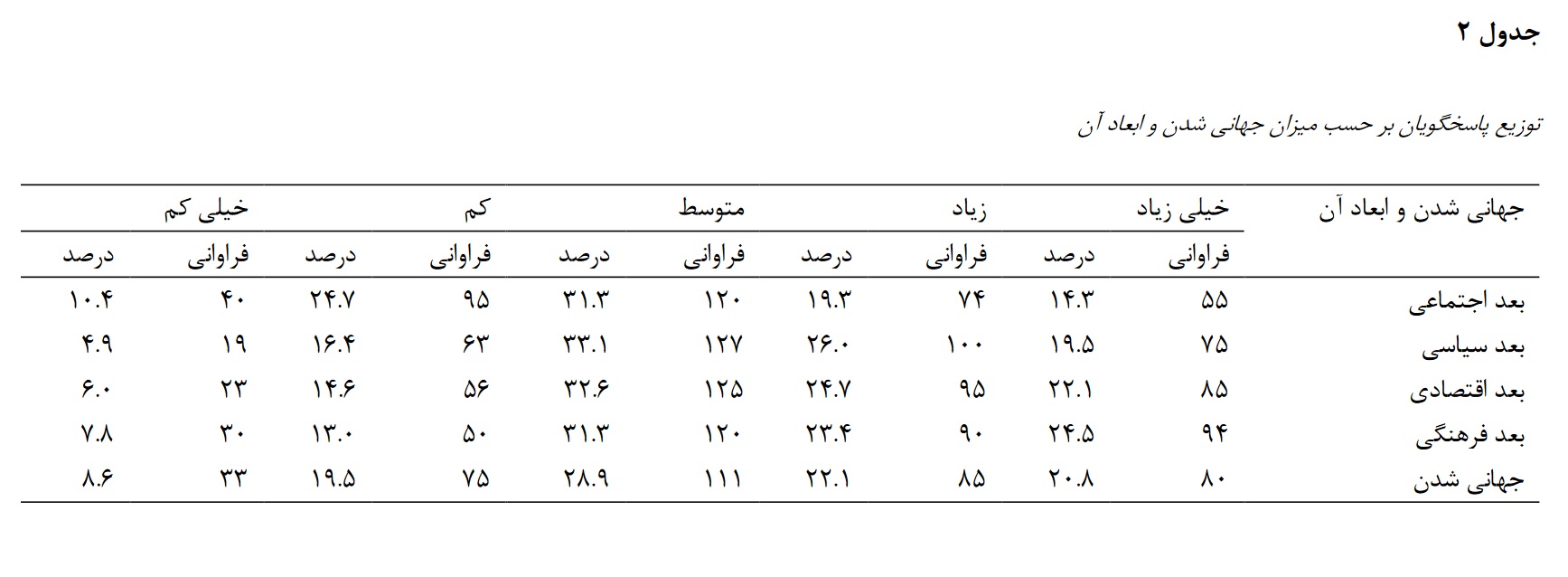
The findings of the research showed that the average citizenship rights among people are relatively high and its average is 3.14. About 36.6 percent consider their citizenship rights to be low. About 26.1% consider the level of citizenship rights to be moderate and about 37.3% to be high. There is a significant positive and direct relationship between globalization and citizenship rights (r=0.378). That is, the more positive the attitude towards globalization becomes, the more citizenship rights increase. The social dimension component of globalization with a coefficient of 0.378 and the economic dimension component with a coefficient of 0.238 have the highest and lowest correlation with citizenship rights, respectively. Globalization and its four dimensions (social, cultural, economic and political) explain and predict about 19.5% of the variance and changes in citizenship rights. The result is that in order to increase the amount of citizenship rights, it is necessary to pay attention to globalization and its dimensions, especially the social dimension of globalization.
Downloads